
Metal 3D printing, also known as metal additive manufacturing, is revolutionizing the production of lightweight components. Unlike previous procedures, which cut away material, this technology builds pieces layer by layer, allowing for the fabrication of complicated and durable components. A significant breakthrough is the development of advanced lightweight metal alloys, such as titanium and aluminum, which provide exceptional strength while significantly reducing weight. These advancements are broadening the applications of metal 3D printing, making it a critical tool for businesses that require both performance and efficiency. Manufacturers can use these materials and techniques to create high-performance parts that match the demanding needs of modern applications.
Importance of lightweight designs in 3D printing
So, why is lightweight design so important? In industries like aerospace and automotive, every ounce counts. Reducing the weight of metal components can result in significant improvements in fuel efficiency and performance. For example, lighter aircraft can fly further and use less fuel, but lighter automotive parts can increase acceleration and handling. Beyond performance, lightweight designs promote sustainability by reducing material and energy use.
By incorporating lightweight metal designs into 3D printing, firms can achieve more efficient production processes and higher-performing goods. This technology does more than simply make things lighter; it also makes them better. As metal 3D printing advances, its impact on numerous industries will only increase, boosting innovation and efficiency across the board.
Innovations in lightweight metal 3D printing
Advanced materials and alloys in lightweight metal printing
The materials used in lightweight metal 3D printing make a significant difference. Recent advances in metal alloys used in SLM technology have substantially increased the capabilities of this technology. New alloys, such as sophisticated titanium and aluminum composites, are specifically engineered to be lightweight while maintaining strength. These materials allow for the creation of parts that are not only lighter, but also more durable and robust.
For example, titanium alloys are well-known for their excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making them perfect for aerospace and high-performance applications. Similarly, aluminum alloys provide superior strength and corrosion resistance while being far lighter than typical steel. These improvements are pushing the boundaries of what is feasible in metal 3D printing, enabling manufacturers to make components that were previously unattainable using traditional methods.
Technological advancements supporting lightweight designs
Beyond materials, technical breakthroughs are propelling the development of lightweight metal 3D printing. Innovations in printing techniques, such as enhanced powder bed fusion and directed energy deposition, are improving printing precision and efficiency. These technologies enable more precise control over the printing conditions, resulting in higher-quality products with optimal weight and strength.
Another major achievement is the creation of sophisticated tools to assist in the design and optimization of lightweight components. Engineers can use tools such as generative design software to produce complicated shapes that use less material while preserving structural integrity. This improves performance while simultaneously lowering waste and production costs.
Applications of lightweight metal 3D printing
Consider the aircraft sector to see how these advances have had an influence. Companies are using lightweight metal 3D printing to create aircraft parts that are up to 50% lighter than conventional components, resulting in significant fuel savings and improved performance. Automotive makers are using lightweight metal designs to increase vehicle efficiency and handling. One famous example is the use of 3D-printed titanium parts in high-performance sports cars, which increases speed and agility while lowering overall weight.
Aerospace industry
In the aerospace industry, lightweight metal 3D printing is having a big impact. The capacity to create lightweight, high-strength components is transforming aircraft design and manufacture. For example, improved titanium and aluminum alloys can be used to make turbine blades and structural supports, which provide higher strength while reducing weight. This results in higher fuel efficiency, greater flight ranges, and better overall performance.
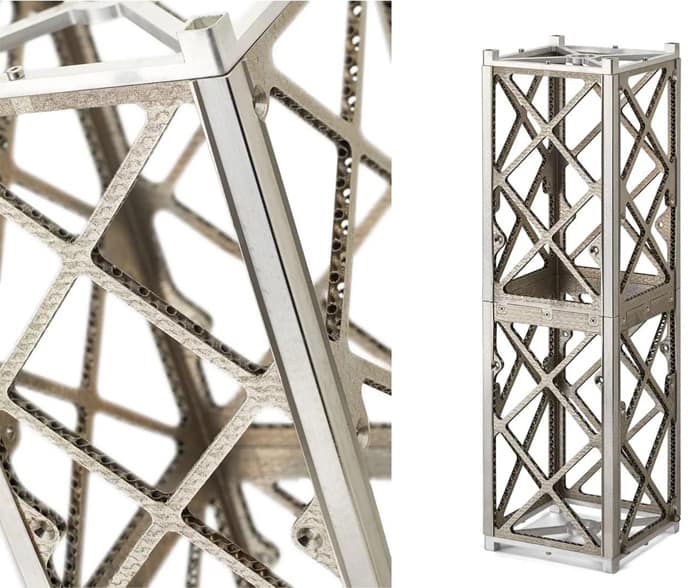

One amazing use is the production of complicated geometries that are difficult to create using regular manufacturing methods. Lightweight metal 3D printing enables the creation of complex, optimized pieces that improve aerodynamic performance and minimize drag. This not only increases aircraft efficiency but also creates new opportunities for novel designs that were previously impossible.
Automotive sector advancements
The automotive sector is also experiencing the benefits of lightweight metal 3D printing technology. Manufacturers are increasingly utilizing sophisticated metal alloys to develop components that enhance vehicle performance and efficiency. To minimize vehicle weight, lightweight metal elements can be employed in engine components, suspension systems, and even body panels. This leads to increased fuel efficiency, faster acceleration, and enhanced handling.
A famous example is the usage of 3D-printed aluminum components in high-performance sports automobiles. These parts offer the strength and endurance required for harsh environments while drastically lowering weight. Automotive manufacturers may provide vehicles that are not only more efficient, but also perform better, by utilizing lightweight metal designs.
Medical devices and implants
In the medical field, lightweight metal 3D printing is revolutionizing the production of implants and medical devices. The use of sophisticated metal alloys enables the development of personalized implants that are suited to the individual demands of patients. These implants have several advantages, including lower weight, higher biocompatibility, and increased durability.
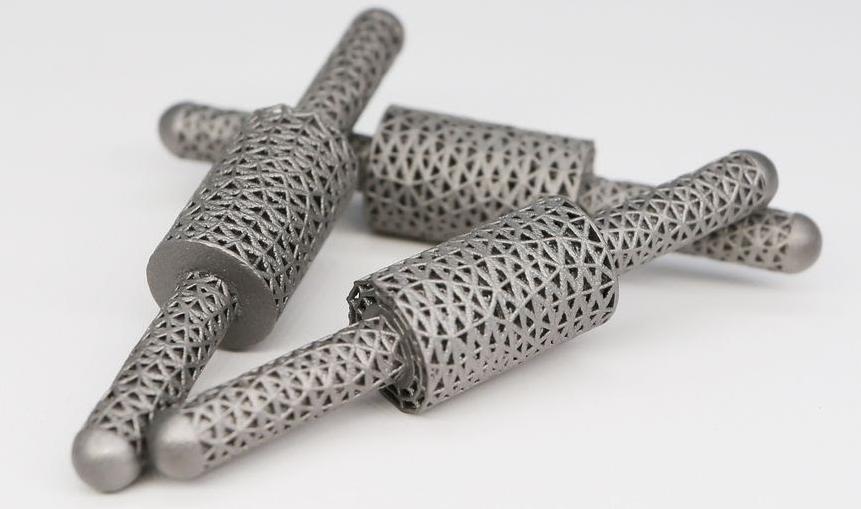

For example, lightweight titanium implants are widely utilized in orthopedic procedures due to its strength and compatibility with the human body. The ability to print these implants with accuracy allows them to be made to fit properly, resulting in improved outcomes and shorter recovery times for patients. Furthermore, lightweight metal 3D printing enables the creation of complicated medical devices that were before impossible to produce.
Consumer electronics
Lightweight metal 3D printing is also making an impact in the consumer electronics market. From smartphones to computers, manufacturers are utilizing lightweight metal designs to make more efficient and visually appealing goods. By using new metal alloys, electronics designers can create lighter, stronger casings and components that improve functionality and longevity.
For example, 3D-printed metal components are used in high-end headphones and wearable gadgets to create a stylish, durable design without adding extra weight. This not only improves user comfort, but also increases product performance and lifetime.
Benefits of lightweight metal designs in 3D printing
Enhanced performance and efficiency
One of the most notable advantages of lightweight metal designs for 3D printing is the huge increase in performance and efficiency they provide. Manufacturers can improve performance across a wide range of applications by reducing component weight. In aerospace, for example, lighter aircraft parts improve fuel efficiency, allowing planes to fly greater distances on less fuel. Similarly, lighter car parts help with acceleration and handling.
The performance improvements do not stop with fuel efficiency and speed. Lightweight metal designs improve the overall efficiency of machinery and equipment. For example, in industrial settings, lighter components can minimize the strain on motors and drives, resulting in lower energy consumption and a longer equipment lifespan. This makes lightweight metal 3D printing not just a choice for performance but also for operational efficiency.
Cost efficiency and savings
Another significant benefit of 3D printing with lightweight metal designs is cost effectiveness. Traditional production methods frequently result in significant material waste and costly machining operations. In contrast, metal 3D printing creates pieces layer by layer, reducing waste and the requirement for post-processing. This leads to cheaper material costs and a more efficient production process.
Furthermore, the ability to produce complicated geometries without the need for extra tooling or molds can result in significant cost savings. For example, in vehicle manufacturing, lightweight 3D-printed parts can minimize the amount of components needed, simplifying assembly and cutting production costs. These savings can be spent in future innovation or passed on to consumers in the shape of lower-cost products.
Sustainability and environmental benefits
Lightweight metal designs in 3D printing provide significant environmental benefits. The reduction in material usage connected with this technology helps to promote more sustainable production methods. Metal 3D printing contributes to the larger goal of lowering the environmental effect of industrial processes by minimizing waste and energy usage.
Furthermore, lightweight components might contribute to lower energy usage in end-use applications. For example, lighter automobiles use less gasoline, while lighter machinery needs less energy. This not only promotes environmental sustainability, but also assists enterprises in meeting regulatory obligations and corporate sustainability objectives.
In conclusion, the advantages of lightweight metal designs in 3D printing go beyond enhanced performance. They provide cost-effectiveness, operational savings, and significant environmental benefits, making them a compelling choice for modern manufacturing across various industries.
Challenges and future directions in lightweight metal 3D printing
Lightweight metal 3D printing has problems such as high costs for advanced alloys and equipment, as well as unpredictability in component quality caused by uneven material qualities and printing conditions. Looking ahead, developments are aimed at making materials more accessible and enhancing printing methods. The incorporation of AI and machine learning is intended to improve process efficiency, part quality, and support for complicated designs. Ongoing research seeks to scale up manufacturing, improve post-processing, and investigate new uses, with industry, academia, and technology providers working together to drive innovation and overcome these issues.
FAQ: Lightweight metal 3D printing
What is lightweight metal 3D printing?
Lightweight metal 3D printing is a manufacturing technology that layers sophisticated metal alloys to build high-performance, lightweight components. This method enables the manufacturing of complicated, strong, and long-lasting parts suitable for a wide range of industrial applications.
What are the benefits of using lightweight metals in 3D printing?
The key advantages are improved performance, such as increased fuel efficiency and vehicle handling, cost savings from less material waste and simpler manufacturing processes, and environmental sustainability by reducing material use and energy consumption.
What are the common metal alloys for lightweight design in 3d printing?
Common metal alloys used for lightweight design in 3D printing include titanium, known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, and aluminum, valued for its lightweight and corrosion resistance. These alloys enable the production of strong, durable components while reducing overall weight, making them ideal for aerospace, automotive, and other high-performance applications.
Which industries benefit most from lightweight metal 3D printing?
Industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical gadgets, and consumer electronics gain greatly. Aerospace employs it for fuel-efficient aircraft parts, automotive for improved vehicle performance, medical for personalized implants, and consumer electronics for sleek and durable components.
What are the latest innovations in lightweight metal 3D printing?
Recent advancements include novel metal alloys that are both strong and lightweight, innovative printing processes such as powder bed fusion, and improved design software that enables optimal, complex shapes. These advances broaden the capabilities and uses of metal 3D printing.
